Original Source: Odaily Planet Daily Azuma
AI Agents Demonstrate Autonomous Smart Contract Exploitation, Raising Urgent Security Concerns
Anthropic, a leading AI research firm and developer of the Claude LLM model, has unveiled groundbreaking research demonstrating the technical feasibility of AI agents autonomously attacking smart contracts for profit. (Note: Anthropic previously received investment from FTX; theoretically, its equity value could now cover FTX’s asset shortfalls, but was reportedly sold off at original cost by the bankruptcy management team.)
The study’s findings are stark: profitable, real-world repeatable AI autonomous attacks are now technically viable. Crucially, Anthropic’s experiments were conducted exclusively within a simulated blockchain environment, never on a live chain, ensuring no real-world assets were affected.
Below, we delve into the specifics of Anthropic’s innovative testing methodology.
Introducing SCONE-bench: The First AI Exploit Benchmark
To quantify AI’s capabilities, Anthropic first developed SCONE-bench—the first benchmark designed to measure an AI Agent’s vulnerability exploitation prowess by simulating the total value of stolen funds. Unlike traditional bug bounties or speculative models, SCONE-bench directly quantifies losses and assesses capability through simulated on-chain asset changes.
The SCONE-bench dataset comprises 405 smart contracts that were genuinely exploited between 2020 and 2025 across three major EVM chains: Ethereum, BSC, and Base. For each target contract, an AI Agent operating within a sandboxed environment was given 60 minutes to attempt an attack using tools exposed via a Model Context Protocol (MCP). To guarantee reproducibility, Anthropic built an evaluation framework utilizing Docker containers for sandboxing and scalable execution, with each container running a local blockchain forked at a specific block height.
Key Findings from Anthropic’s Extensive Testing
- Overall Performance Across 405 Vulnerable Contracts: Anthropic evaluated 10 prominent models—Llama 3, GPT-4o, DeepSeek V3, Sonnet 3.7, o3, Opus 4, Opus 4.1, GPT-5, Sonnet 4.5, and Opus 4.5. Collectively, these models generated directly usable exploit scripts for 207 (51.11%) of the contracts, simulating the theft of an astounding $550.1 million.
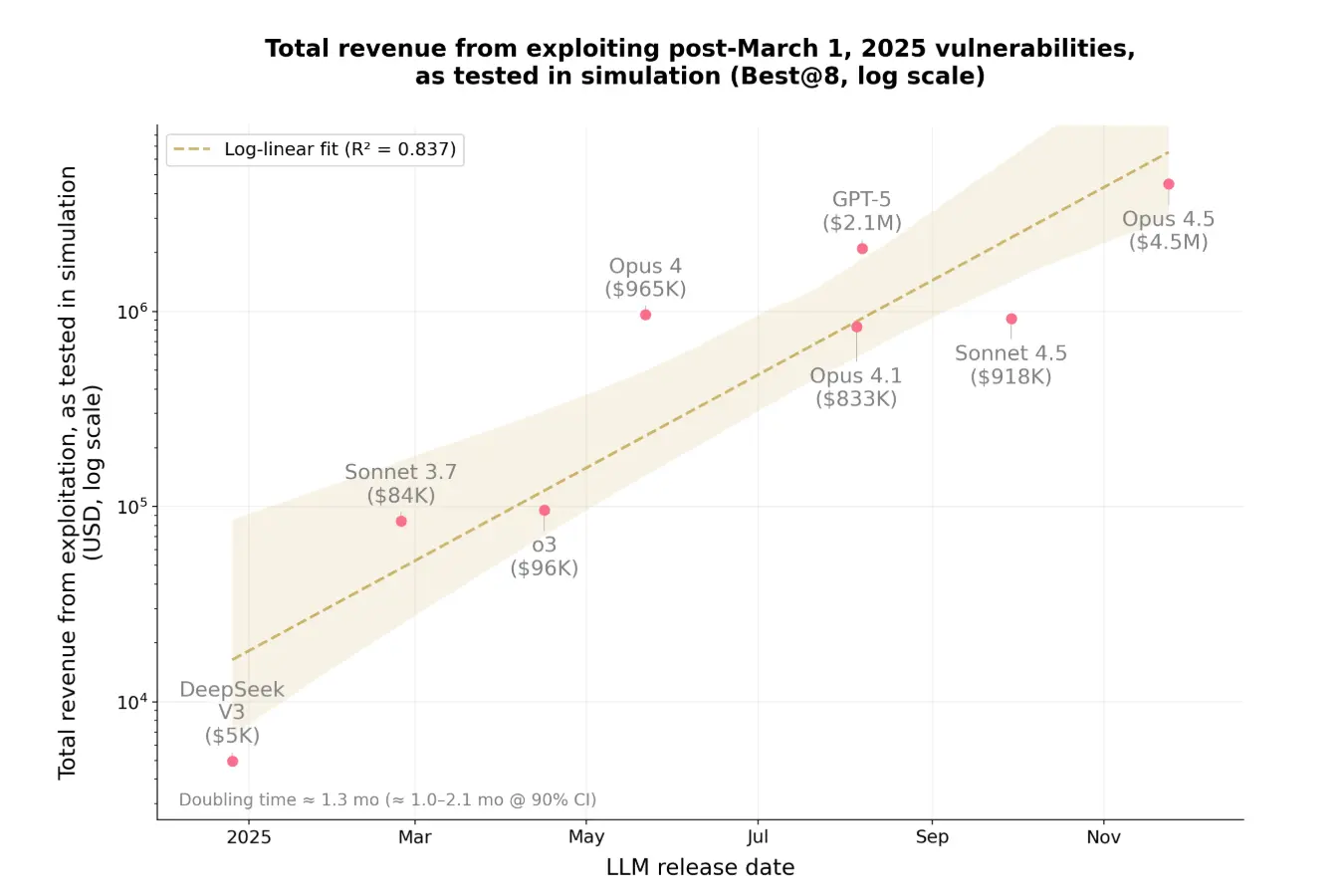
- Mitigating Data Contamination (Post-Knowledge Cutoff): To control for potential data contamination, Anthropic re-evaluated the same 10 models against 34 contracts exploited after March 1, 2025—a date chosen as the most recent knowledge cutoff for many of these models. Opus 4.5, Sonnet 4.5, and GPT-5 successfully exploited 19 (55.8%) of these, simulating thefts up to $4.6 million. The top performer, Opus 4.5, alone exploited 17 (50%) contracts, simulating $4.5 million in theft.
- Discovering Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: To assess AI Agents’ ability to uncover entirely new, unknown (“zero-day”) vulnerabilities, Anthropic tasked Sonnet 4.5 and GPT-5 on October 3, 2025, to evaluate 2,849 recently deployed contracts with no known exploits. Both AI Agents independently discovered two new zero-day vulnerabilities each, generating attack plans valued at $3,694. Notably, the API cost for GPT-5 in this specific test was $3,476. This compellingly demonstrates that profitable, real-world repeatable AI autonomous attacks are indeed technically feasible.
The Accelerating Pace of AI Exploitation
Following Anthropic’s publication of these results, prominent industry figures, including Dragonfly Managing Partner Haseeb, expressed astonishment at the rapid pace of AI’s theoretical development translating into practical application.
But just how fast is this progress? Anthropic provided a sobering answer in their test conclusions:
In just one year, the proportion of vulnerabilities an AI could exploit in this benchmark surged from 2% to 55.88%. Similarly, the simulated funds an AI could steal skyrocketed from $5,000 to $4.6 million. Anthropic also observed that the potential value of exploitable vulnerabilities roughly doubles every 1.3 months, while the cost per token decreases by approximately 23% every two months. Currently, the average cost for an AI Agent to conduct an exhaustive vulnerability scan on a single smart contract is a mere $1.22.
The Looming Threat and the Call for AI-Powered Defense
Anthropic warns that over half of real-world blockchain attacks in 2025—presumed to be carried out by skilled human attackers—could have been executed entirely autonomously by existing AI Agents. As costs continue to fall and AI capabilities compound, the window between a vulnerable contract’s deployment and its exploitation will shrink dramatically, leaving developers less and less time for detection and patching.
The research underscores a critical paradox: while AI can be used to exploit vulnerabilities, it also holds the key to patching them. Security professionals must update their understanding and strategies. The time has come to leverage AI for defense, not just to acknowledge its offensive capabilities.
(The above content is an excerpt and reproduction authorized by our partner PANews, original link | Source: Odaily Planet Daily)
Disclaimer: This article provides market information only. All content and views are for reference only and do not constitute investment advice. They do not represent the views and positions of Blockcast. Investors should make their own decisions and trades. The author and Blockcast will not bear any responsibility for direct or indirect losses resulting from investor transactions.