This report is authored by Tiger Research.
As Bitcoin prices experience recent downward pressure, market attention has sharply pivoted to the largest institutional holders of Bitcoin, often referred to as DAT companies. Among these, Strategy stands out as a preeminent player. The critical questions revolve around how this company has amassed its substantial Bitcoin reserves and, more importantly, how it plans to navigate and manage risk in an increasingly volatile market landscape.
Executive Summary
- Strategy’s projected static bankruptcy threshold for 2025 is approximately $23,000, nearly double its 2023 level of $12,000.
- Since 2024, the company has diversified its financing model, moving from simple cash and minor convertible bonds to a more complex mix including convertible bonds, preferred stock, and At-The-Market (ATM) offerings.
- Investor put options embedded in convertible bonds allow for early redemption. A significant decline in Bitcoin price could trigger these options, making 2028 a crucial risk window for Strategy.
- Should refinancing efforts fail in 2028, and assuming a Bitcoin price of $90,000, Strategy might be compelled to sell approximately 71,000 Bitcoins. This volume, representing 20% to 30% of daily average trading, would exert substantial pressure on the broader market.
1. Unpacking Strategy’s Stability Amidst Market Turmoil
The recent downturn in Bitcoin prices has triggered a roughly 50% decline in the stock valuations of DAT companies. This volatility has brought a fundamental market question to the forefront: Can Strategy maintain its stability when both its equity and core underlying asset (Bitcoin) are depreciating? Concerns were further amplified by JPMorgan’s assessment of Strategy’s potential removal from MSCI indices.
The market’s focus extends beyond mere stock performance. Strategy’s immense Bitcoin holdings are of a scale that can significantly influence the broader cryptocurrency market, far exceeding the impact of a typical “whale” investor. This unique position prompts two critical inquiries:
- At what Bitcoin price point would Strategy’s balance sheet become unsustainable?
- When and under what circumstances could the company’s financial actions exert a measurable impact on the market?
To address these questions, this report meticulously reviews Strategy’s U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filings. Our objective is to identify the company’s effective bankruptcy threshold, pinpoint periods of heightened risk, and assess the potential market repercussions should stress scenarios materialize.
2. Strategy’s Critical Risk Point: The $23,000 Threshold
Before delving into our analysis, it’s crucial to define the concept of static bankruptcy. Static bankruptcy refers to a state where a company’s total liabilities exceed the value of all its assets, even if those assets were fully liquidated.
In essence, static bankruptcy occurs when assets fall short of covering debts. For instance, if a company holds property worth $1 billion and $100 million in cash but carries $1.2 billion in debt, it is balance-sheet insolvent. DAT companies face a similar predicament: if Bitcoin’s price drops below a specific level, their book equity turns negative, rendering them unable to service their debts. This critical price point is known as the static bankruptcy threshold.
To ascertain Strategy’s static bankruptcy threshold, we first examined its Bitcoin accumulation strategy.
Strategy adopted Bitcoin as a strategic asset in 2020, but its accumulation methodology underwent a significant transformation post-2023. Prior to this, the company primarily funded Bitcoin purchases through cash reserves and modest convertible bond issuances. Its holdings remained below 100,000 BTC, and refinancing needs were relatively contained.
A pivotal shift in Strategy’s financing model occurred in 2024. The company began leveraging a diversified mix of preferred stock issuances, At-The-Market (ATM) equity programs, and large-scale convertible bonds to raise capital for aggressive Bitcoin acquisitions.
This strategic pivot dramatically accelerated Bitcoin accumulation. The structure fostered a self-reinforcing cycle: higher Bitcoin prices inflated the company’s market capitalization, enabling greater leverage, which in turn funded further Bitcoin purchases. While the underlying objective remained Bitcoin accumulation, the funding architecture and inherent risk profile evolved significantly. This structural metamorphosis now stands as a central factor intensifying Strategy’s bankruptcy risk.
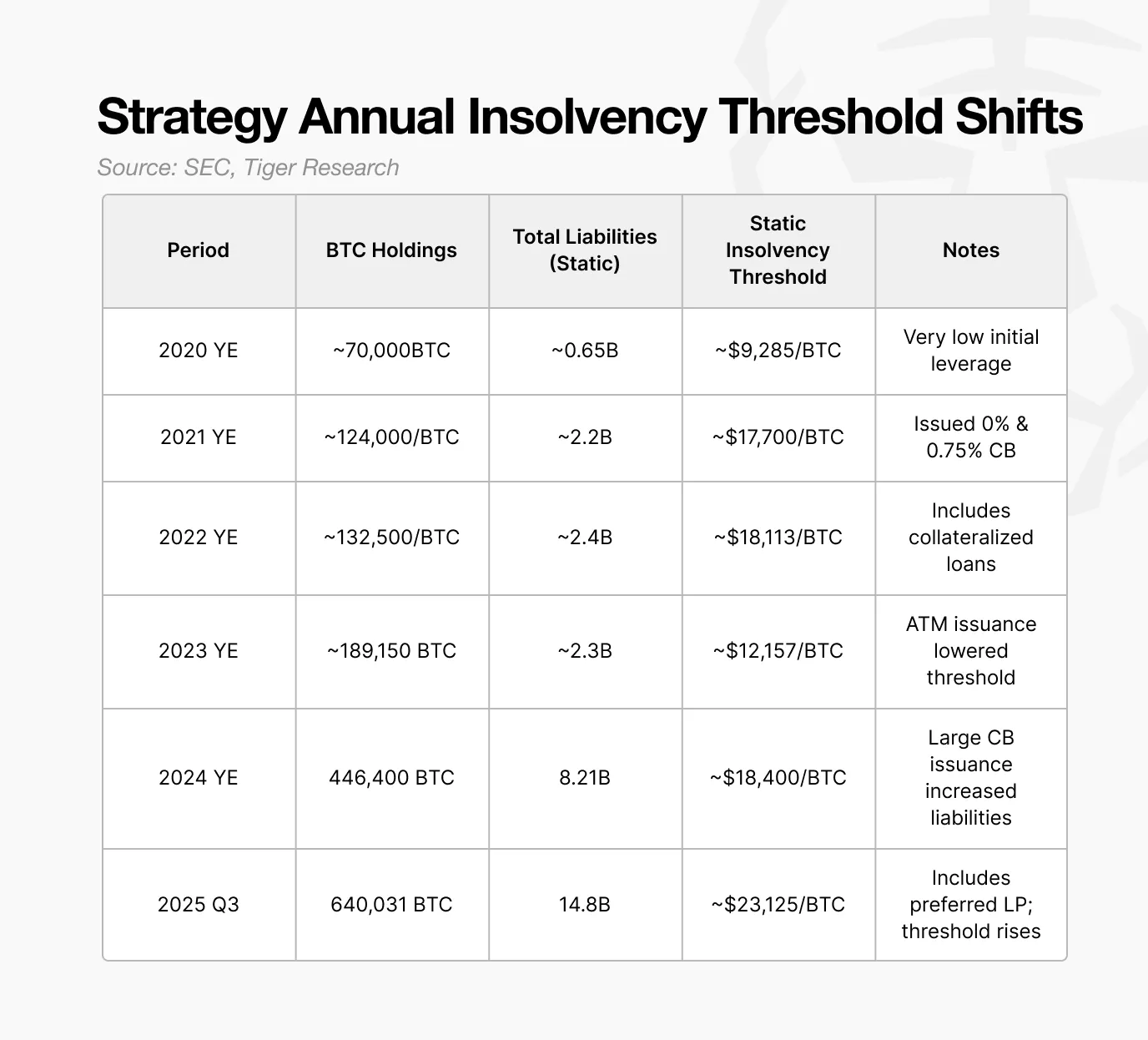
For 2025, Strategy’s static bankruptcy threshold is estimated to be approximately $23,000. Below this price, the aggregate value of its Bitcoin holdings would fall below its total liabilities, pushing the company into balance sheet insolvency.
Crucially, this threshold has been on an upward trajectory. In 2023, the company could withstand a Bitcoin price of around $12,000. This benchmark rose to $18,000 in 2024, and is projected to reach $23,000 by 2025. As Strategy continues to expand its Bitcoin portfolio, this critical floor price escalates proportionally.
Therefore, the $23,000 threshold signifies the minimum Bitcoin price required for Strategy to maintain stable operations. This implies that Bitcoin would need to experience a roughly 73% decline from current levels to trigger this specific bankruptcy risk.
3. Convertible Bonds: The Put Option, Not Maturity, Is the Key
As previously established, Strategy’s static bankruptcy threshold has climbed to $23,000, driven by its debt growth outpacing the value of its Bitcoin holdings. The subsequent crucial inquiry is into the specific architecture of these debt instruments.
Between 2024 and 2025, Strategy adopted a novel financing framework, integrating convertible bonds, preferred stock, and ATM equity programs. Among these instruments, convertible bonds represent the most substantial component and carry the most pronounced implications for market stability.
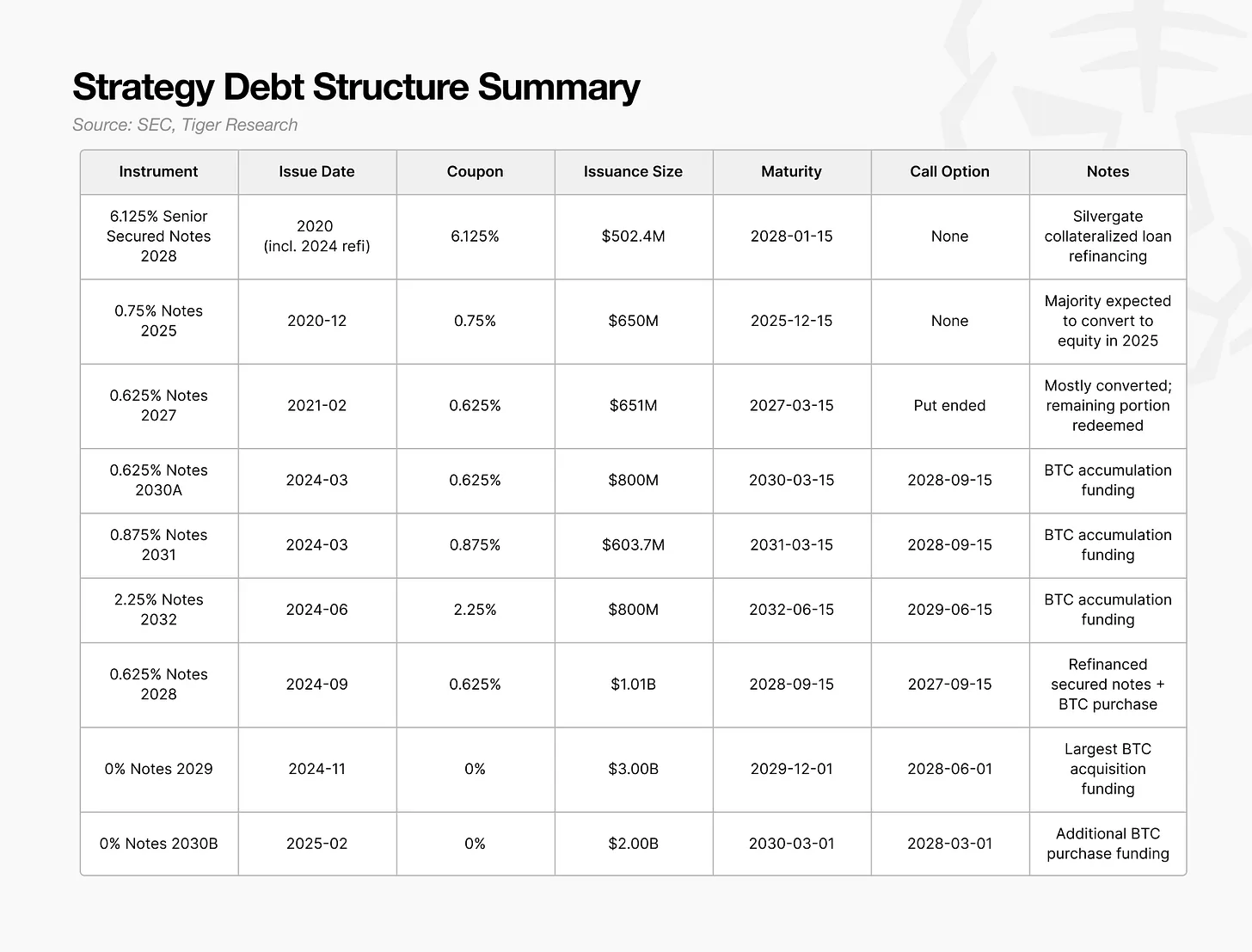
The pivotal factor for these convertible bonds is not their total size or scheduled maturity dates, but rather the timing of the holders’ embedded put options (redemption rights).
This critical clause empowers investors to demand early repayment, an obligation the company cannot refuse. A significant portion of the large convertible bonds issued in 2024-2025 have their holder redemption dates concentrated around 2028. Consequently, 2028 emerges as a singularly critical year for Strategy to demonstrate its refinancing capabilities.
Should Bitcoin prices hover near the bankruptcy threshold in 2028 or if broader market conditions deteriorate, investors are highly likely to exercise these put options rather than await maturity. A cascade of put option exercises would necessitate Strategy to immediately secure billions of dollars in cash.
A fundamental challenge arises from the allocation of these funds: almost all capital raised through these convertible bonds was channeled directly into Bitcoin purchases. Had these funds been invested in productive, cash-generating assets, the company would naturally possess a robust source for repayment. However, Strategy’s singular focus on Bitcoin accumulation has left it with minimal liquid cash reserves available for debt redemption.
Therefore, any significant debt repayment would inevitably require the sale of assets. If Bitcoin prices are depressed when these option windows open, Strategy could face an immediate and severe liquidity crisis. Such forced selling would further depress Bitcoin prices, potentially elevating the effective bankruptcy threshold and triggering a detrimental feedback loop.
4. Preferred Stock: The Rationale Behind a 10% Dividend Burden
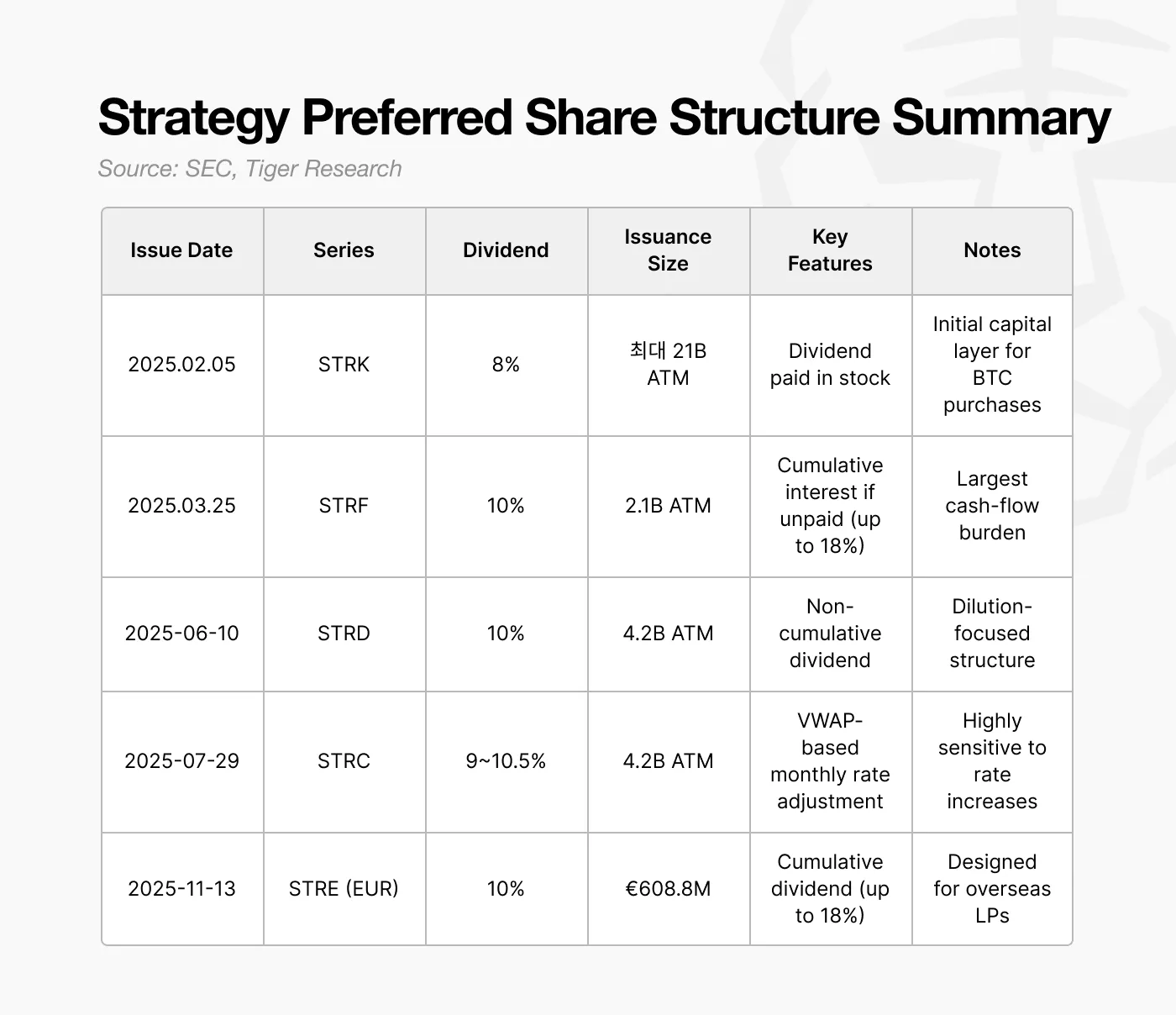
Starting in 2025, Strategy shifted its financing approach, moving from issuing near-zero-coupon convertible bonds to preferred stock with an approximate 10% dividend yield. At first glance, this appears to be a considerably more expensive financing choice.
However, this decision strategically reflects the escalating refinancing pressures anticipated in the 2027-2028 timeframe. The concentration of bondholder put options in 2028 significantly amplifies the medium-term repayment risk. Any sustained cash outflows during this period would invariably heighten the company’s bankruptcy vulnerability.
The key distinguishing feature of this preferred stock lies in its dividend structure: dividends are not strictly required to be paid in cash. Strategy’s issuance is engineered to allow dividend payments to be made in additional stock when necessary. This mechanism enables the company to raise capital without an immediate cash drain and to fulfill its dividend obligations without depleting its cash reserves. In essence, preferred stock serves as a crucial tool for Strategy to potentially circumvent the need to sell Bitcoin during the critical 2027-2028 period.
While a 10% dividend rate appears steep, the flexibility to pay dividends in stock transforms it into a vital instrument for preserving liquidity and mitigating short-term cash shortages.
Nevertheless, this structure introduces new challenges. The payment of dividends in stock invariably leads to continuous dilution for common shareholders. Strategy already faces potential equity dilution from the future conversion of its convertible bonds, and preferred stock adds another layer of pressure on existing equity holders.
Furthermore, preferred stock holders enjoy priority in repayment. Should the company face simultaneous pressure from debt servicing and operational costs, preferred shareholders’ claims must be satisfied before common shareholders. Although preferred stock lacks a fixed maturity date, its dividend obligations constitute a structural fixed cost, thereby influencing the company’s effective bankruptcy threshold.
By 2024-2025, Strategy has fundamentally transitioned from a model predominantly reliant on low-cost convertible bonds to a hybrid structure that strategically combines convertible bonds, preferred stock, and ATM issuances. This strategic pivot has facilitated a rapid expansion of its Bitcoin holdings in the short term, albeit with an altered risk profile.
5. The Domino Effect: What Happens If Strategy Fails?
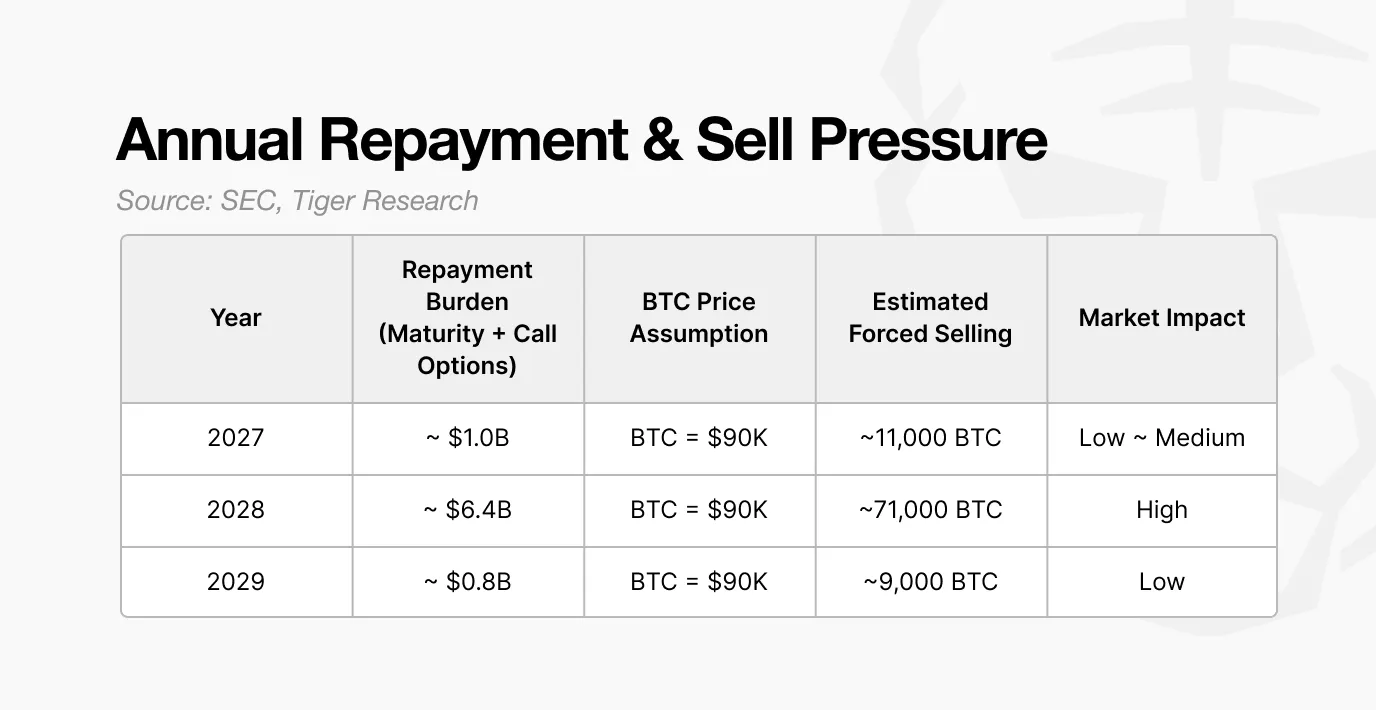
Should Strategy fail to secure refinancing in 2028, the potential market impact can be quantified by its substantial repayment obligations.
The significant volume of convertible bonds issued between 2024 and 2025 will give rise to an estimated $6.4 billion in potential repayment demands in 2028. If market conditions deteriorate to a point where new preferred stock issuances, ATM offerings, or additional convertible bonds become infeasible, the company would be left with no recourse but to liquidate its Bitcoin holdings.
Assuming a Bitcoin price of $90,000, Strategy would be required to sell approximately 71,000 Bitcoins to satisfy these obligations. This is a volume that dwarfs typical institutional sales.
Currently, the daily average trading volume in the Bitcoin spot market ranges from $20 billion to $30 billion. A sale of 71,000 Bitcoins at a $90,000 price point translates to roughly $6.4 billion, representing an astounding 20% to 30% of the daily trading volume. Such a massive, concentrated sell-off over a short period would almost certainly exert severe downward price pressure on the market.
More alarmingly, such a liquidation event would not be a one-off occurrence. As Bitcoin prices fall, the value of Strategy’s remaining assets would immediately shrink, weakening its financial ratios. This would further cripple its ability to raise capital and potentially force it into additional Bitcoin sales.
The outcome is a perilous feedback loop: refinancing failure leads to forced selling, forced selling triggers price declines, price declines diminish asset value, compelling the company to sell even more assets. This dynamic, if sustained for several quarters, could irrevocably deteriorate the balance sheet.
Therefore, Strategy’s structural risk is acutely concentrated in 2028. Beyond this critical window, the leveraged model appears manageable. However, a failure to refinance in 2028 could unleash selling pressure potent enough to destabilize the entire Bitcoin market.
Consequently, 2028 is not merely vital for Strategy’s corporate survival but also a pivotal year for the potential volatility and stability of the broader Bitcoin ecosystem.
6. Strategy’s Relative Stability, Higher Risks for Newer Entrants
Market narratives frequently oversimplify the risks associated with DAT companies, often reducing them to a singular question: can a firm merely survive successive Bitcoin price corrections? However, this analysis underscores that a company’s resilience hinges not on short-term price fluctuations or stock volatility, but fundamentally on the strength of its balance sheet and the strategic design of its capital structure.
Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of DAT companies demands a perspective beyond mere stock price or Bitcoin price dips. Crucial indicators include the precise positioning of their static bankruptcy threshold, the timing of significant cash repayment pressures, and the specific financial instruments employed to bridge potential funding gaps. These factors collectively offer a deeper understanding of structural resilience, transcending transient market movements.
It is important to acknowledge that not all risks are perfectly predictable. Evolving ETF fund flows, shifts in macroeconomic conditions, and changes in regulatory policy can instantaneously reshape the market environment. Even amidst such uncertainties, the most reliable benchmarks remain the bankruptcy thresholds implied by robust financial data and the company’s foundational cash flow mechanisms.
In this context, Strategy occupies a distinctive position. Having entered the Bitcoin market in 2020, the company successfully navigated the 2022 downturn and subsequently accelerated its accumulation through sophisticated leveraged financing in 2024. Its strategic combination of convertible bonds and preferred stock has effectively constructed a multi-layered buffer mechanism against adverse market conditions.
As such, Strategy benefits from a relatively stable foundation. In stark contrast, newer entrants to the DAT space, lacking a mature framework and established financing structures, possess significantly less stable resilience against substantial price declines.
(The above content is excerpted and reproduced with authorization from our partner PANews. Original Link | Source: Tiger Research)
Disclaimer: This article is provided for market information purposes only. All content and opinions are for reference only and do not constitute investment advice. They do not represent the views or positions of Blockcast. Investors should make their own decisions and trades. The author and Blockcast will not bear any responsibility for direct or indirect losses incurred by investors’ transactions.